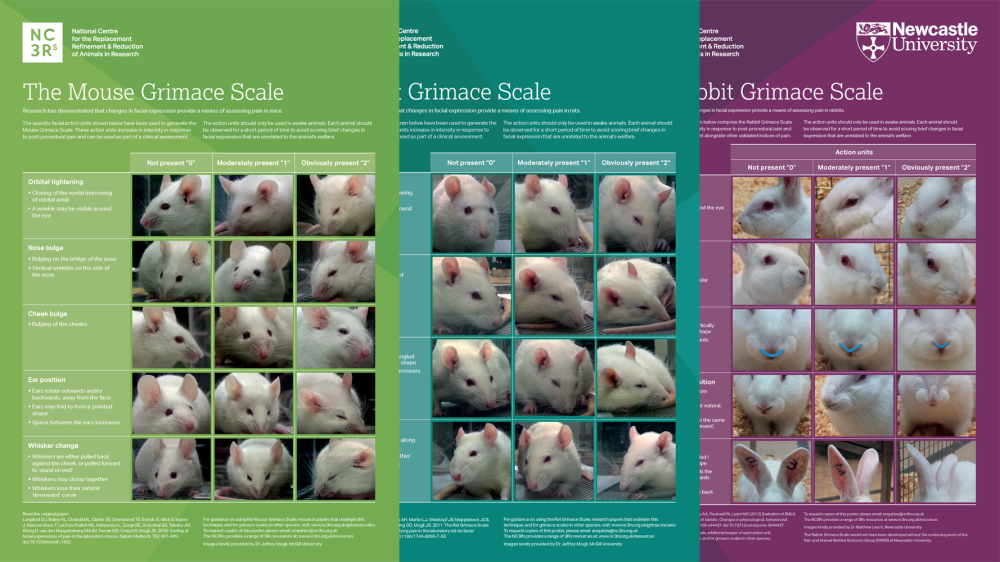
Grimace scale: Rat
The rat grimace scale features specific facial action units, increasing in intensity in response to post-procedural pain. These can be used as part of a clinical assessment.
Research has demonstrated that changes in facial expression provide a means of assessing pain in many laboratory species including the mouse, rat and rabbit.
We have produced a poster featuring the rat grimace scale to help familiarise staff with the specific facial action units, and encourage their implementation as a means of welfare assessment.
Read the original paper
Sotocinal SG et al. (2011). The Rat Grimace Scale: a partially automated method for quantifying pain in the laboratory rat via facial expressions. Molecular Pain 7: 55. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-7-55
Available posters
We have copies of The Rat Grimace Scale poster in a number of languages. Downloadable copies are subject to the T&Cs outlined below.
Download terms and conditions
The proper use of a grimace scale poster requires each of the facial action units to be clear and easily discernible. They therefore must be printed by a professional print service at the full A3 size. Further guidance is included in the cover page which should not be removed from the PDF file.
Any requests to reproduce this poster, or to include it in any publications or training materials, should be directed to enquiries@nc3rs.org.uk. You should include how, why and where the poster will be used so that we can consider your case for approval. It is helpful to include any associated text, so we can see the context in which the poster will be put.
Copyright notice: These posters and their content are owned by the NC3Rs and its partners. The poster should not be adapted, and the content should not be sold or used to generate income.
Papers that validate or use this technique
References
- Chi H et al. (2013). Postoperative pain impairs subsequent performance on a spatial memory task via effects on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in aged rats. Life Sciences 93(25-26): 986-993. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2013.10.028
- Liao L et al. (2014). Evaluation of pain in rats through facial expression following experimental tooth movement. European Journal of Oral Sciences 122(2): 121-124. doi:10.1111/eos.12110
- Kawano T et al. (2014). Effects of ketoprofen for prevention of postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged rats. Journal of Anaesthesia 28(6): 932-936. doi:10.1007/s00540-014-1821-y
- Oliver V et al. (2014). Psychometric assessment of the Rat Grimace Scale and development of an analgesic intervention score. PLOS ONE 16(9): e97882. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0097882
- Préfontaine L et al. (2015). Postoperative pain in Sprague Dawley rats after liver biopsy by laparotomy versus laparoscopy. Lab Animal 44(5): 174-178. doi:10.1038/laban.731
- De Rantere D et al. et al. (2015). The relationship between the Rat Grimace Scale and mechanical hypersensitivity testing in three experimental pain models. European Journal of Pain 20(3): 417-26. doi:10.1002/ejp.742
- Whittaker AL et al. et al. (2015). Effects of acute chemotherapy-induced mucositis on spontaneous behaviour and the grimace scale in laboratory rats. Laboratory Animals 50(2): 108-18. doi:10.1177/0023677215595554
- Waite ME et al. (2015). Efficacy of common analgesics for postsurgical pain in rats. Journal of the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science 54(4): 420-425. PMID:26224443
- Gao M et al. (2015). The role of periodontal ASIC3 in orofacial pain induced by experimental tooth movement in rats. European Journal of Orthodontics 38(6): 577-583. doi:10.1093/ejo/cjv082
- Yousef MA et al. (2015). Successful reconstruction of nerve defects distraction neurogenesis with a new experimental device. Basic and Clinical Neuroscience 6(4): 253-264. PMID:26649163
- Asgar J et al. (2015). The role of TRPA1 in muscle pain and mechanical hypersensitivity under inflammation conditions in rats. Neuroscience 310: 206-215. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.09.042
- Long H et al. (2015). Periodontal CGRP contributes to orofacial pain following experimental tooth movement in rats. Neuropeptides 52: 31-37. doi:10.1016/j.npep.2015.06.006
- Kawano T et al. (2016). Effects and underlying mechanisms of endotoxemia on post-incisional pain in rats. Life Sciences 148: 145-153. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2016.01.046
- Leung V et al.(2016). Real-time application of the Rat Grimace Scale as a welfare refinement in laboratory rats. Scientific Reports 6: 31667. doi:10.1038/srep31667
- Miller AL et al. (2016). The influence of isoflurane anaesthesia on the Rat Grimace Scale. PLOS ONE 11(11): e0166652. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0166652
- Finlayson K et al. (2016). Facial indicators of positive emotions in rats. PLOS ONE 11(11): e0166446. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0166446
- Saine L et al. (2016). Effects of fentanyl on pain and motor behaviors following a collagenase-induced intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Journal of Pain Research 9: 1039-1048. doi:10.2147/JPR.S121415
- Schneider LE et al. (2016). Application of the rat grimace scale as a marker of supraspinal pain sensation after cervical spinal cord injury. Journal of Neurotrauma 34(21): 2982-2993. doi:10.1089/neu.2016.4665
- Long H et al. (2017). A novel technique of delivering viral vectors to trigeminal ganglia in rats. European Journal of Oral Sciences 125(1): 1-7. doi:10.1111/eos.12326
- Philips BH et al. (2017). Use of the rat grimace scale to evaluate neuropathic pain in a model of cervical radiculopathy. Comparative medicine 67(1): 34-42. PMID: 28222837
- Jeger V et al. (2017). Improving animal welfare using continuous nalbuphine infusion in a long-term rat model of sepsis. Intensive Care Medicine Experimental 5(1): 23. doi:10.1186/s40635-017-0137-2
- Yamanaka D et al. (2017). The preventive effects of dexmedetomidine on endotoxin-induced exacerbated post-incisional pain in rats. Journal of Anesthesia 31(5): 664-671. doi:10.1007/s00540-017-2374-7
- Gao Z et al. (2017). Local infiltration of the surgical wounds with levobupivacaine, dexibuprofen, and norepinephrine to reduce postoperative pain: A randomized, vehicle–controlled, and preclinical study. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 92: 459-467. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.038
- Senko T et al. (2017). Angiotensin II enhancement during pregnancy influences the emotionality of rat offspring (Rattus norvegicus) in adulthood. Potential use of the Rat Grimace Scale. Neuro Endocrinology Letters 38(2): 117-123. PMID: 28650605
- Akintola T et al. (2017). The grimace scale reliably assesses chronic pain in a rodent model of trigeminal neuropathic pain. Neurobiology of Pain 2: 13-17. doi:10.1016/j.ynpai.2017.10.001
- Guo P and Hu SP (2017). Thalidomide alleviates postoperative pain and spatial memory deficit in aged rats. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 95: 583-588. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.114
- Khoo SY et al. (2018). Local anaesthetic refinement of pentobarbital euthanasia reduces abdominal writhing without affecting immunohistochemical endpoints in rats. Laboratory animals 52(2): 152-162. doi:10.1177/0023677217721260
- Fujita M et al. (2018). Allopregnanolone suppresses mechanical allodynia and internalization of neurokinin-1 receptors at the spinal dorsal horn in a rat postoperative pain model. Korean Journal of Pain 31(1): 10-15. doi:10.3344/kjp.2018.31.1.10
- Sperry MM et al. (2018). Grading facial expression is a sensitive means to detect grimace differences in orofacial pain in a rat model. Scientific Reports 8(1): 13894. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-32297-2
- Chaves RHF et al. (2018). Influence of tramadol on functional recovery of acute spinal cord injury in rats. Acta Cirúrgica Brasileira 33(12): 1087-1094. doi:10.1590/s0102-865020180120000006
- Cheng Y et al. (2018). Antinociceptive effects of the adenylyl cyclase inhibitor ST034307 on tooth-movement-induced nociception in rats. Archives of Oral Biology 98: 81-86. doi:10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.11.012
- de Barros Silva PG et al. (2019). Tumor necrosis factor alpha mediates orofacial discomfort in an occlusal dental interference model in rats: the role of trigeminal ganglion inflammation. Journal of Oral Pathology and Medicine 49(2): 169-176. doi:10.1111/jop.12984
- Wilkinson CM et al. (2019). The collagenase model of intracerebral hemorrhage in awake, freely moving animals: the effects of isoflurane. Brain Research 6: 146593. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146593
- Nagakura Y et al. (2019). Spontaneous pain-associated facial expression and efficacy of clinically used drugs in the reserpine-induced rat model of fibromyalgia. European Journal of Pharmacology 864: 172716. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172716
- George RP et al. (2019). Use of the Rat Grimace Scale to evaluate visceral pain in a model of chemotherapy-induced mucositis. Animals (Basel) 9(9). doi:10.3390/ani9090678
- Shinozuka K et al. (2019). Empathy in stroke rats is modulated by social settings. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 271678X19867908. 0.1177/0271678X19867908
- Harikrishnan VS et al. (2019). A novel technique to develop thoracic spinal laminectomy and a methodology to assess the functionality and welfare of the contusion spinal cord injury (SCI) rat model. PLOS One 14(7): e0219001. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0219001
- Klune CB et al. (2019). Comparing the Rat Grimace Scale and a composite behaviour score in rats. PLOS One 14(5): e0209467. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0209467
- Leung VSY et al. (2019). Performance of behavioral assays: the Rat Grimace Scale, burrowing activity and a composite behavior score to identify visceral pain in an acute and chronic colitis model. Pain Reports 4(2): e718. doi:10.1097/PR9.0000000000000712
- Uddin O et al. (2019). Chronic pain after blast-induced traumatic brain injury in awake rats. Neurobiology of Pain 6: 100030. doi:10.1016/j.ynpai.2019.100030
- Akintola T et al. (2019). In search of a rodent model of placebo analgesia in chronic orofacial neuropathic pain. Neurobiology of Pain 6: 100033. doi:10.1016/j.ynpai.2019.100033
- Koyama T et al. (2019). Acute postoperative pain exacerbates neuroinflammation and related delirium-like cognitive dysfunction in rats. Journal of Anesthesia 33(3): 482-486. doi:10.1007/s00540-019-02635-3
- Guo R et al. (2019). Transient receptor potential Vanilloid 1-based gene therapy alleviates orthodontic pain in rats. International Journal of Oral Science 11(1): 11. doi:10.1038/s41368-019-0044-3
- Zhang EQ et al. (2019). Influence of rater training on inter- and intrarater reliability when using the rat grimace scale. Journal of the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science 58(2): 178-183. doi:10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-18-000044
- Klune CB et al. 2020. Hypothermia During General Anesthesia Interferes with Pain Assessment in Laboratory Rats (Rattus norvegicus). Journal of the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science 59(6): 719-725. doi:10.30802/aalas-jaalas-20-000018
Read more about why the grimace scales were developed, and download the scales for use with mice and rats.